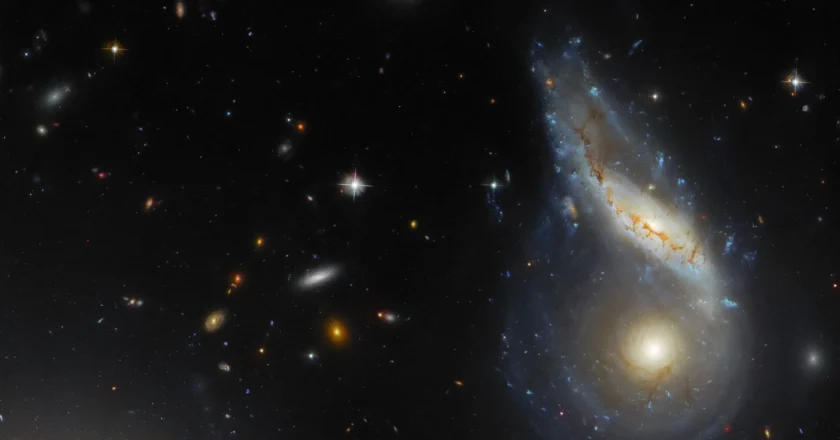
Hubble Captures Amazing Image of Dwarf Galaxy Known As UGC 4879
The Hubble Space Telescope continues to prove itself useful. In a image the telescope captures, we can see the dwarf galaxy known as UGC 4879.UGC 4879 is located four million light years way. Astronomers have been studying it to determine if it's a undisturbed galaxy.They theorize that these low mass galaxies may have been the first to form. If this galaxy truly is old, it could provide clues to the evolution of other galaxies, and even the universe itself.